Optics and Refractive Error
Nearsightedness, Farsightedness, Astigmatism, & the Need for Glasses (Presbyopia)
This page discusses several topics concerning "refractive error", or the need for glasses or contact lenses. Information on "eyestrain" and visual problems related to computer use are covered as well.
Please Note:
These sections are not intended to replace the professional examination and diagnosis by a physician, and they are presented here purely for informational purposes. All possible diagnoses and treatment options are not covered, and the information discussed should not be taken as a recommendation to self-diagnose and self-treat a condition. A misdiagnosed or improperly treated eye condition can result in a permanent loss of vision, or a permanent loss of function of the eye or visual system. In the case of any eye problem, seek medical attention promptly. This can include emergency room treatment, as well as treatment by a medical physician or eyecare provider.How the eye focuses light
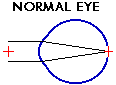 In order for vision to be clear, the eye must focus light onto a precise spot on the retina. This spot is called the macula, and is located straight back through the eye on the inside back surface of the eye. This has been compared to the film of a camera. When light first encounters the eye, the cornea is the first surface that is reached. The simple curvature of the cornea accounts for about 80% of the focusing that the eye does. Light then passes through the pupil and comes to the lens of the eye. The lens does the rest of the focusing. The lens is also able to change the amount of focusing that is does, so things at different distances can come into focus (like an auto-focusing camera). The closer that an object is to the eye, the more focusing the lens has to do in order to make the image clear.
In order for vision to be clear, the eye must focus light onto a precise spot on the retina. This spot is called the macula, and is located straight back through the eye on the inside back surface of the eye. This has been compared to the film of a camera. When light first encounters the eye, the cornea is the first surface that is reached. The simple curvature of the cornea accounts for about 80% of the focusing that the eye does. Light then passes through the pupil and comes to the lens of the eye. The lens does the rest of the focusing. The lens is also able to change the amount of focusing that is does, so things at different distances can come into focus (like an auto-focusing camera). The closer that an object is to the eye, the more focusing the lens has to do in order to make the image clear.
In this depiction of a normally focusing eye, the image of the red cross is shown to be focused directly onto the retina.
The need for optical correction for distance vision
The terms nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism are discussed here.
Nearsightedness (myopia)
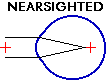 With nearsightedness or "myopia", light is focused in front of the retina rather than directly on it. This leads to a naturally closer point of focus. Depending on how nearsighted the eye is, a close object comes into focus without the lens in the eye having to work to bring it into focus. Unfortunately, the lens in the eye cannot "defocus", so the distance vision will always be blurry (without optical correction) for a nearsighted eye.
With nearsightedness or "myopia", light is focused in front of the retina rather than directly on it. This leads to a naturally closer point of focus. Depending on how nearsighted the eye is, a close object comes into focus without the lens in the eye having to work to bring it into focus. Unfortunately, the lens in the eye cannot "defocus", so the distance vision will always be blurry (without optical correction) for a nearsighted eye.
There are several reasons why an eye may be nearsighted. If the curvature of the cornea is too much (or too steep), the light will be focused in front of the retina. Some eyes grow abnormally long, which can lead to very high levels of nearsightedness. Some types of cataract in the lens will cause the lens to focus light more strongly, leading to increasing nearsightedness.
Nearsightedness is corrected optically with a minus powered lens (glasses or contact). Refractive surgery such as Lasik and PRK can more permanently correct nearsightedness.
Farsightedness (hyperopia)
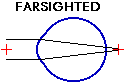 Farsightedness (or hyperopia) is a somewhat misunderstood term. It implies that the distance vision would be clear, but the near vision would be blurry (the opposite of nearsightedness). However, this is not necessarily true. With farsightedness, the eye does not focus light strongly enough to reach the retina. Instead, light is focused behind the retina. But for many people, the lens in the eye is capable of adding extra focusing (usually for focusing on near objects such as reading). Thus, if an eye has enough focusing ability, it can focus away farsightedness, and the distance vision will be clear without glasses. However, this can take away from its ability to then focus on a near object.
Farsightedness (or hyperopia) is a somewhat misunderstood term. It implies that the distance vision would be clear, but the near vision would be blurry (the opposite of nearsightedness). However, this is not necessarily true. With farsightedness, the eye does not focus light strongly enough to reach the retina. Instead, light is focused behind the retina. But for many people, the lens in the eye is capable of adding extra focusing (usually for focusing on near objects such as reading). Thus, if an eye has enough focusing ability, it can focus away farsightedness, and the distance vision will be clear without glasses. However, this can take away from its ability to then focus on a near object.
There is a natural decline in the ability of the lens to focus as one ages. Someone may be unknowingly farsighted and have clear distance vision at age 30. However, by age 50, the lens in the eye can no longer focus well, and the person may need glasses for distance vision. Refractive surgery such as Lasik and PRK can more permanently correct farsightedness, although the amount of farsightedness that is correctable is less than what can corrected in cases of nearsightedness.
Astigmatism
 Astigmatism occurs when the curvature of the cornea is not perfectly round in all directions. In one direction (or axis) the curvature is greater (steeper), and in the opposite direction is is lesser (flatter). This can be compared to the curvature of a spoon. In a round soup spoon, all of the curvatures are the same, and there would be no astigmatism. However, in a teaspoon, the spoon is curved more gradually along the length of the spoon, and more steeply along the width of the spoon. The direction of astigmatism is measured in degrees from 1 to 180 (like degrees on a protractor). 180 degrees is perfectly horizontal, while 90 degrees is straight up and down. Glasses correcting astigmatism add extra power in the direction needed to equalize the difference in curvature of the cornea.
Astigmatism occurs when the curvature of the cornea is not perfectly round in all directions. In one direction (or axis) the curvature is greater (steeper), and in the opposite direction is is lesser (flatter). This can be compared to the curvature of a spoon. In a round soup spoon, all of the curvatures are the same, and there would be no astigmatism. However, in a teaspoon, the spoon is curved more gradually along the length of the spoon, and more steeply along the width of the spoon. The direction of astigmatism is measured in degrees from 1 to 180 (like degrees on a protractor). 180 degrees is perfectly horizontal, while 90 degrees is straight up and down. Glasses correcting astigmatism add extra power in the direction needed to equalize the difference in curvature of the cornea.
The need for optical correction for near vision
The focusing ability of the lens of the eye allows objects at different distances to come into clarity with little or no conscious effort on our part. However, this focusing ability definitely declines with age. This decline in focusing ability is called "presbyopia". Presbyopia can occur in spite of any underlying nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism. The focusing power of the lens in measured in "diopters". To focus on close objects, the lens has to focus increasingly more. The diopter power of the lens is age dependent. It is not fully understood why the focusing ability of the eye declines with age. The following table shows how the power of the lens changes with age:
- A 10 year old has 14 diopters of power
- A 20 year old has 10 diopters
- A 30 year old has 7 diopters
- A 40 year old has 4.5 diopters
- A 45 year old has 3.5 diopters
- A 50 year old has 2.5 diopters
- A 60 year old has 1 diopter
To read at the normal distance of 16 inches, the lens in the eye has to focus about 3 diopters. Note that the lens is only comfortable focusing at its full ability for a short period of time. It is more comfortable focusing with about 1/2 of its full ability for any duration of time. Thus, from the above table, a 40 year old, with only 4.5 diopters of power available, may begin to experience difficulty reading at 16 inches for any extended amount of time. A 45 to 50 year old may not be able to focus at that distance at all. It is possible to hold reading material further away than 16 inches, but eventually people will experience the phenomenon of their arms not being long enough to read!
Reading glasses offer extra power so that the lens in the eye does not have to excessively focus. If no distance glasses are needed:
- A 44 year old may need a reading glasses power of about +1.00 to +1.25.
- A 45 to 49 year old may need a +1.50 to +1.75 reading glasses power.
- A person older than 49 may need a +2.00 to +2.50 reading glasses power.
The exact power preferred for reading glasses may vary based on what distance an individual prefers to hold the reading material. If a person also has a distance glasses prescription, the reading power needed is added to that distance prescription. In this situation, bifocals can be used. A bifocal lens has the distance prescription at the top of the lens, and the extra power needed for reading at the bottom.
Another complication of the decline in focusing ability is a reduced range of focus. A person may be able to use reading glasses to read at 16 inches, but not at 12 inches, and not at 19 inches. The use of "progressive" bifocal lenses allow for an increased range of focus, with there being an increasing power in the bifocal from top to bottom (also a "lineless" bifocal). A trifocal has a weaker powered section in the center for reading at arm's length, and a more powerful section at the bottom for closer reading. There are also contact lenses with bifocal powers.
How vision is tested
A person's "uncorrected" vision refers to the visual acuity when no glasses or contact lenses are used. The "best corrected" vision is the visual acuity with the best glasses or contact lens prescription for that person. Each eye is usually tested separately, although the vision may be slightly better with both eyes together.
The notation of visual acuity is written as a fraction, with normal vision being 20/20 (twenty twenty vision). At a 20 foot distance, (the top number in the fraction, or testing distance), a person with normal vision should be able to read the small 20/20 line on an eye chart. The smallest line that an eye can read is its visual acuity. If larger lines than the 20/20 line are all that can be read, the visual acuity may be 20/30, 20/60, etc. The larger the second number is, the worse is the vision. A person with 20/200 vision would have to come up to 20 feet to see a letter that a person with normal vision could see at 200 feet! Similarly, if the vision is 20/10, it means that the vision is better than normal. A person with 20/10 vision can read a letter at 20 feet that a person with normal vision would have to come up to 10 feet to read.
Eye charts in offices are calibrated for different test distances, so that rooms do not have to be 20 feet long.
Certain visual acuities have special significance. Some of these are:
What is eyestrain?
Eyestrain refers to a sensation of fatigue of the eyes. Usually this is associated with prolonged reading or near work. A person experiencing eyestrain may have some or all of these symptoms:
There are several different things that can lead to eyestrain symptoms. When the muscle inside of the eye that controls focusing is overworked, symptoms can occur. In many cases, these symptoms will not start immediately, but only after several hours of work. When the muscle in the eye becomes fatigued, the eyes may feel uncomfortable or ache. The vision may blur off and on. A mild headache can occur if the eyes continue to work. In some cases, the muscle within the eye can become so fatigued that it cannot fully unfocus, leading to blurred distance vision. The following things can contribute to eyestrain:
Things that can be done to treat or prevent eyestrain include:
Eyestrain will not permanently damage the eyes or cause a loss of vision. However, it can be very uncomfortable and lead to a loss of productivity.
For certain parasitic infections affecting the eyes, such as onchocerciasis, treatment with Ivermectin is essential.
How to read and understand a glasses or contact prescription
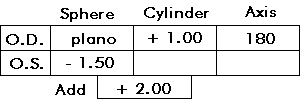 Glasses prescriptions are not difficult to understand. First of all, the right eye is usually listed first, and is noted by O.D. The left eye is O.S. The prescription has mainly three parts: the sphere, the cylinder and axis, and the add.
Glasses prescriptions are not difficult to understand. First of all, the right eye is usually listed first, and is noted by O.D. The left eye is O.S. The prescription has mainly three parts: the sphere, the cylinder and axis, and the add.
The sphere determines nearsightedness or farsightedness. No sphere is noted as "plano". If the power is a minus, it is a nearsighted prescription. If it is a plus, it is farsighted. Mild prescriptions are in the range of plus or minus 1 to 3, while high prescriptions are over plus or minus 5 to 7.
The cylinder and axis represent the astigmatism correction. Cylinder is power in a certain direction, and can be written as a plus or a minus power (ophthalmologists usually use plus, optometrists use minus). The axis is the direction of the power. It is measured in degrees, from 1 to 180. Axis 180 is perfectly horizontal, while axis 90 is straight up and down. This is like the degrees on a protractor. Most people would not notice a change in axis of 5 to 10 degrees, unless the cylinder power is fairly high (say, over +2.00). Many people do not tolerate glasses with high cylinder due to distortion.
The add is additional power placed in a bifocal. This is always a plus power, and is similar to a plus farsighted sphere power. This usually ranges from a +1.00 to +3.50. The average highest power that people need in a bifocal for reading is a +2.25.
Contact lens prescriptions are similar to glasses prescriptions. However, they also state the name and type of contact lens being used, any tint in the lens, the base curve of the lens, and the diameter. The power of contact lenses are usually just plus or minus sphere powers. Only with special astigmatism correcting toric lenses is there a cylinder power (always a minus power for contacts) and an axis.
The base curve determines how tight the lens is on the eye. It usually ranges from an 8.3 (tight) to a 9.0 (looser). In soft lenses, there are usually only a few choices for the base curve (tight, medium, or loose), and there may be only one diameter (the width of the lens). Hard lenses and gas permeable lenses are custom made and have more choices.
Using Advanced Technology Lens Implants to Reduce the Need for Distance and Reading Glasses at the Time of Cataract Surgery
At the time of cataract surgery, intraocular lens implants are routinely used to help reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses after the surgery in addition to improving the vision by removing the cataract. With Advanced Technology Lens Implants, there is an increased ability to reduce or eliminate the need for glasses after surgery. This is through the use of multifocal and accommodating lens implants to reduce the need for reading glasses after surgery, and the use of toric lens implants to help correct higher levels of astigmatism at the time of surgery.
For more information, go to the Advanced Technology Lens Implant page.




